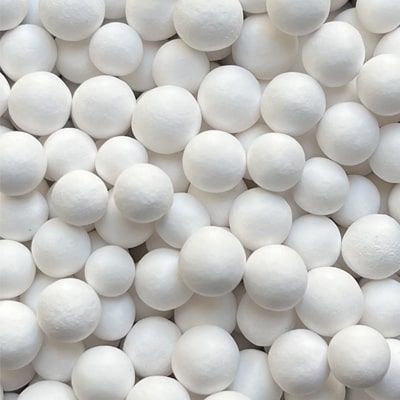

Activated Alumina
Activated alumina, a highly efficient adsorbent, serves as a crucial protective barrier for gas-phase molecular sieve beds. Renowned for its exceptional volumetric capacity, it adeptly absorbs liquids, preventing detrimental effects such as film coating and accelerated coking induced by hydrocarbon condensates, amine, glycol carryover, and liquid water entrainment.
Silica Gel
Silica gel, composed of irregularly shaped, porous silicon dioxide particles, boasts an impressive internal surface area, providing ample sites for adsorption. This desiccant’s chemical inertness ensures stability, making it ideal for various applications. Operating via physical adsorption, silica gel traps moisture molecules within its network of pores without undergoing chemical changes, thereby preventing the formation of byproducts.

Alumina Silica Gel
Silica alumina gel, also termed silica-alumina oxide gel, is a meticulously engineered porous material forged through high-temperature activation. Renowned for its chemical stability, non-flammability, and insolubility across solvents, it emerges in two variants: H type and WS type. Unlike conventional porous silica gel, silica-alumina gel exhibits diminished moisture adsorption at low relative humidity (e.g., RH = 10%, RH = 20%).

3A Molecular Sieve
3A Molecular Sieve, a synthetic A-type zeolite with a potassium-based structure, excels in moisture removal due to its crystalline porous framework with 3 Angstrom pore diameters. It selectively adsorbs water molecules while minimizing the intake of other substances, making it ideal for purification and dehydration in various industries such as petrochemicals, natural gas processing, and air drying applications.

4A Molecular Sieve
4A molecular sieve, is a crystalline alkali metal aluminosilicate, features a pore aperture of approximately 4 angstroms. Predominantly found in its sodium form, this Type A sieve exhibits superior physical and adsorption properties. Renowned for its efficacy as a desiccant, it proficiently adsorbs water, ammonia, methanol, ethanol, and carbon dioxide molecules.

5A Molecular Sieve
The 5A molecular sieve, a calcium-exchanged alkali metal aluminosilicate zeolite with a pore size of 5 angstroms, exhibits remarkable adsorption properties owing to strong ionic forces from the divalent calcium cation. Its efficacy lies in selectively removing carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, alcohols, hydrogen sulfide, methyl and ethyl mercaptans, and other polar molecules.

13X Molecular Sieve
The 13X molecular sieve, derived from sodium zeolite X, boasts expansive pores with a 10-angstrom diameter, surpassing the dimensions of type A crystals. Its remarkable pore size facilitates superior adsorption capabilities, outperforming common adsorbents. With unparalleled theoretical capacity and exceptional mass transfer rates, 13X demonstrates heightened efficacy in purifying gases and liquids.

CaX Molecular Sieve
Calcium X (CaX) and Calcium LSX (CaLSX) molecular sieves are the calcium-exchanged forms of the 13X and LSX-type zeolites. They will adsorb molecules with a kinetic diameter of less than 9 Angstrom (0.9nm) and exclude molecules larger than 0.9nm. CaX and LSK molecular sieves are crucial in various industrial processes.

LiX Molecular Sieve
Lithium X molecular sieve stand as a cornerstone in gas separation science, finding widespread utility in both industrial and medical domains. Their unique molecular structure, characterized by a network of interconnected pores, enables highly efficient adsorption and desorption of gases. These sieves exhibit exceptional nitrogen capacity, rapid kinetics, and unparalleled selectivity, facilitating the generation of high purity oxygen.

Carbon Molecular Sieve
Carbon molecular sieve (CMS) is a specialized material akin to zeolite, featuring precise pore sizes ideal for gas separation. Created through the pyrolysis of organic sources like polymers or biomass, CMS can be fashioned into membranes of various structures. CMS has been pivotal in commercializing pressure swing adsorption for nitrogen-air separation.
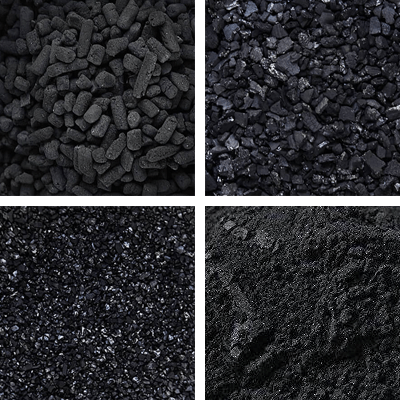

Activated Carbon
Activated carbon is extensively used in the oil and gas industry for various applications. It effectively removes contaminants like H2S/CO2 and degradation compounds from natural gas streams, prolonging equipment life and optimizing performance in amine and glycol recovery processes. Additionally, activated carbon aids in condensate purification, preventing boiler feedwater contamination and maximizing plant efficiency.

Activated Alumina
Activated alumina, a highly efficient adsorbent, serves as a crucial protective barrier for gas-phase molecular sieve beds. Renowned for its exceptional volumetric capacity, it adeptly absorbs liquids, preventing detrimental effects such as film coating and accelerated coking induced by hydrocarbon condensates, amine, glycol carryover, and liquid water entrainment.

Silica Gel
Silica gel, composed of irregularly shaped, porous silicon dioxide particles, boasts an impressive internal surface area, providing ample sites for adsorption. This desiccant’s chemical inertness ensures stability, making it ideal for various applications. Operating via physical adsorption, silica gel traps moisture molecules within its network of pores without undergoing chemical changes, thereby preventing the formation of byproducts

Silica Alumina Gel
Silica alumina gel, also termed silica-alumina oxide gel, is a meticulously engineered porous material forged through high-temperature activation. Renowned for its chemical stability, non-flammability, and insolubility across solvents, it emerges in two variants: H type and WS type. Unlike conventional porous silica gel, silica-alumina gel exhibits diminished moisture adsorption at low relative humidity (e.g., RH = 10%, RH = 20%).

3A Molecular Sieve
3A Molecular Sieve, a synthetic A-type zeolite with a potassium-based structure, excels in moisture removal due to its crystalline porous framework with 3 Angstrom pore diameters. It selectively adsorbs water molecules while minimizing the intake of other substances, making it ideal for purification and dehydration in various industries such as petrochemicals, natural gas processing, and air drying applications.

4A Molecular Sieve
4A molecular sieve, is a crystalline alkali metal aluminosilicate, features a pore aperture of approximately 4 angstroms. Predominantly found in its sodium form, this Type A sieve exhibits superior physical and adsorption properties. Renowned for its efficacy as a desiccant, it proficiently adsorbs water, ammonia, methanol, ethanol, and carbon dioxide molecules.

5A Molecular Sieve
The 5A molecular sieve, a calcium-exchanged alkali metal aluminosilicate zeolite with a pore size of 5 angstroms, exhibits remarkable adsorption properties owing to strong ionic forces from the divalent calcium cation. Its efficacy lies in selectively removing carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, alcohols, hydrogen sulfide, methyl and ethyl mercaptans, and other polar molecules. Moreover, it demonstrates efficient bulk separation of normal and iso-paraffin hydrocarbons.

13X Molecular Sieve
The 13X molecular sieve, derived from sodium zeolite X, boasts expansive pores with a 10-angstrom diameter, surpassing the dimensions of type A crystals. Its remarkable pore size facilitates superior adsorption capabilities, outperforming common adsorbents. With unparalleled theoretical capacity and exceptional mass transfer rates, 13X demonstrates heightened efficacy in purifying gases and liquids.

CaX Molecular Sieve
Calcium X (CaX) and Calcium LSX (CaLSX) molecular sieves are the calcium-exchanged forms of the 13X and LSX-type zeolites. They will adsorb molecules with a kinetic diameter of less than 9 Angstrom (0.9nm) and exclude molecules larger than 0.9nm. CaX and LSK molecular sieves are crucial in various industrial processes.

LiX Molecular Sieve
Lithium X molecular sieve stand as a cornerstone in gas separation science, finding widespread utility in both industrial and medical domains. Their unique molecular structure, characterized by a network of interconnected pores, enables highly efficient adsorption and desorption of gases.

Carbon Molecular Sieve
Carbon molecular sieve (CMS) is a specialized material akin to zeolite, featuring precise pore sizes ideal for gas separation. Created through the pyrolysis of organic sources like polymers or biomass, CMS can be fashioned into membranes of various structures. CMS has been pivotal in commercializing pressure swing adsorption for nitrogen-air separation.

Activated Carbon
Activated carbon is extensively used in the oil and gas industry for various applications. It effectively removes contaminants like H2S/CO2 and degradation compounds from natural gas streams, prolonging equipment life and optimizing performance in amine and glycol recovery processes.

